What Sets Michelin and Bridgestone Apart as the World’s Leading Tire Makers?
Explore how Michelin and Bridgestone compete as global tire giants through unique strategies—Michelin with sustainability and premium focus, Bridgestone with large-scale operations, cutting-edge R&D, and performance innovation across regions.

In the highly competitive global tire industry, two giants, Michelin and Bridgestone stand out as leaders, each employing distinct strategies to maintain their market dominance. Michelin is renowned for its commitment to sustainability, with a focus on eco-friendly tire solutions and innovation in green technologies. On the other hand, Bridgestone’s strength lies in its expansive operational scale, technological advancements, and a strong focus on high-performance products.
Comparing Operational Strength of Tire Giants
Both Michelin and Bridgestone are industry leaders with vast global operations and advanced manufacturing and research facilities. To understand their manufacturing and R&D strength, it's important to delve deeper into their regional presence, technological advancements, and operational capacities.
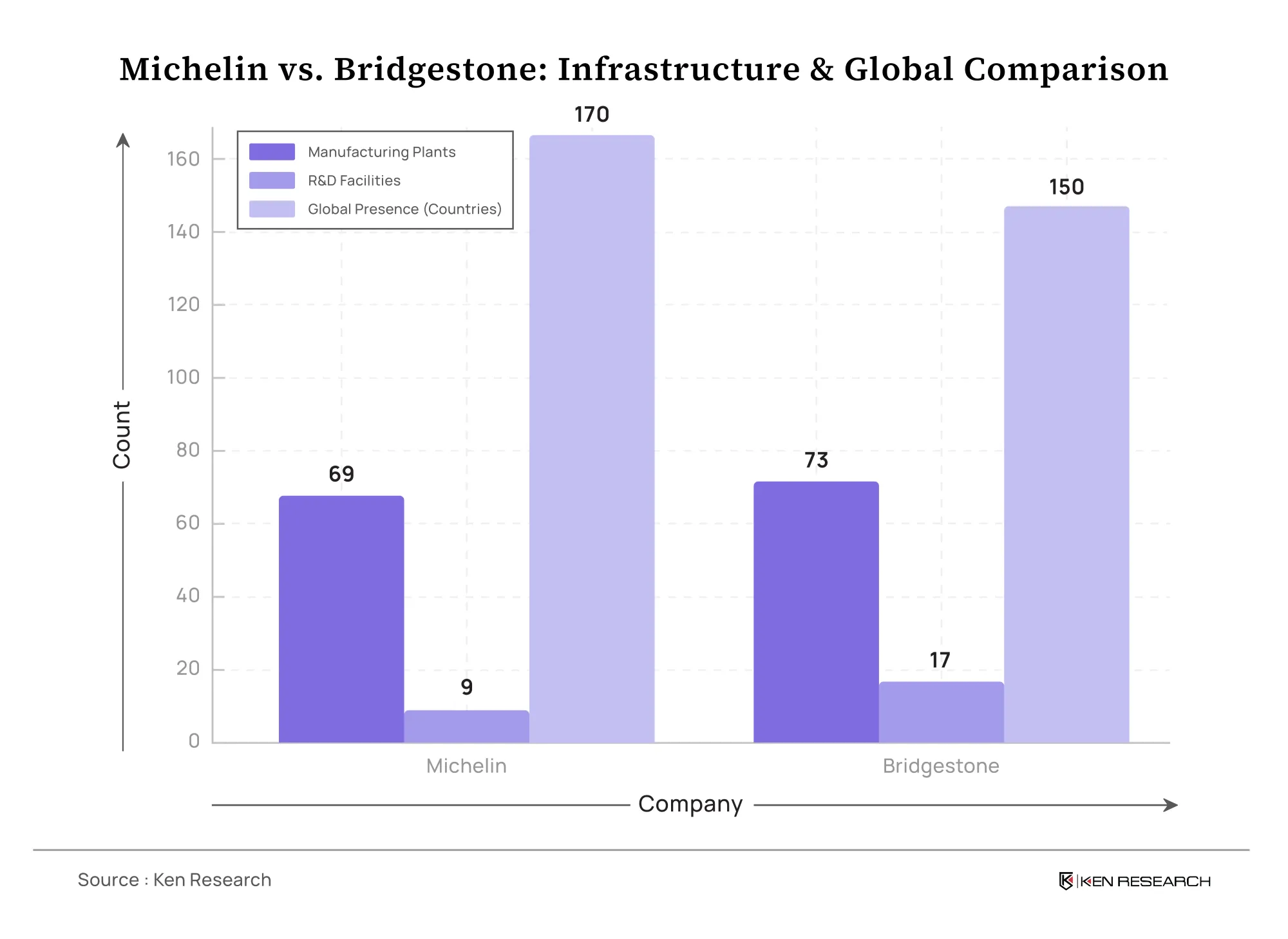
Bridgestone’s Scale: Bridgestone operates 73 tire manufacturing plants globally, which is the largest in the industry. In 2023, Bridgestone produced approximately 530,000 metric tons of rubber tires in the Americas and 470,000 metric tons in Japan, its two largest production regions. This gives Bridgestone a competitive edge in production capacity, enabling faster response times and greater flexibility in managing local markets.
Bridgestone's manufacturing plants are more regionally focused, enabling it to customize production according to local demands and quickly respond to changes in market needs. Its strategic positioning in important regions such as North America, Europe, and Asia also enhances its distribution network.
Michelin’s Reach: Michelin, while operating fewer plants (69), outpaces Bridgestone in global reach. Michelin has a presence in 170 countries, which shows its extensive distribution capabilities and dominant market share in critical regions like Europe, North America, and emerging markets in Asia-Pacific. Michelin’s strategy focuses on long-term growth in mature markets, where it holds strong brand equity.
R&D Infrastructure: Bridgestone’s commitment to R&D is apparent with 17 R&D centers, compared to Michelin’s 9 centers. This larger R&D presence positions Bridgestone to drive faster innovation, including smart tires and next-generation tire materials.
Michelin, while having fewer R&D facilities, has invested heavily in sustainability technologies, which has strengthened its leadership in eco-friendly tire solutions, such as tire recycling and low-carbon tire production.
Financial Performance: Revenue and Profitability
The financial health of both Michelin and Bridgestone is key to understanding their ability to invest in innovation, expansion, and long-term strategic goals. The tire industry is highly capital-intensive, so financial strength directly impacts market leadership.
Michelin’s Revenue Leadership: Michelin leads in total revenue with $30.4 billion, a significant margin over Bridgestone’s $27.43 billion. This reflects Michelin’s strength in high-margin premium tire products, including commercial, passenger, and specialty tires. Michelin's ability to leverage its global network and brand loyalty is evident in its robust revenue growth.
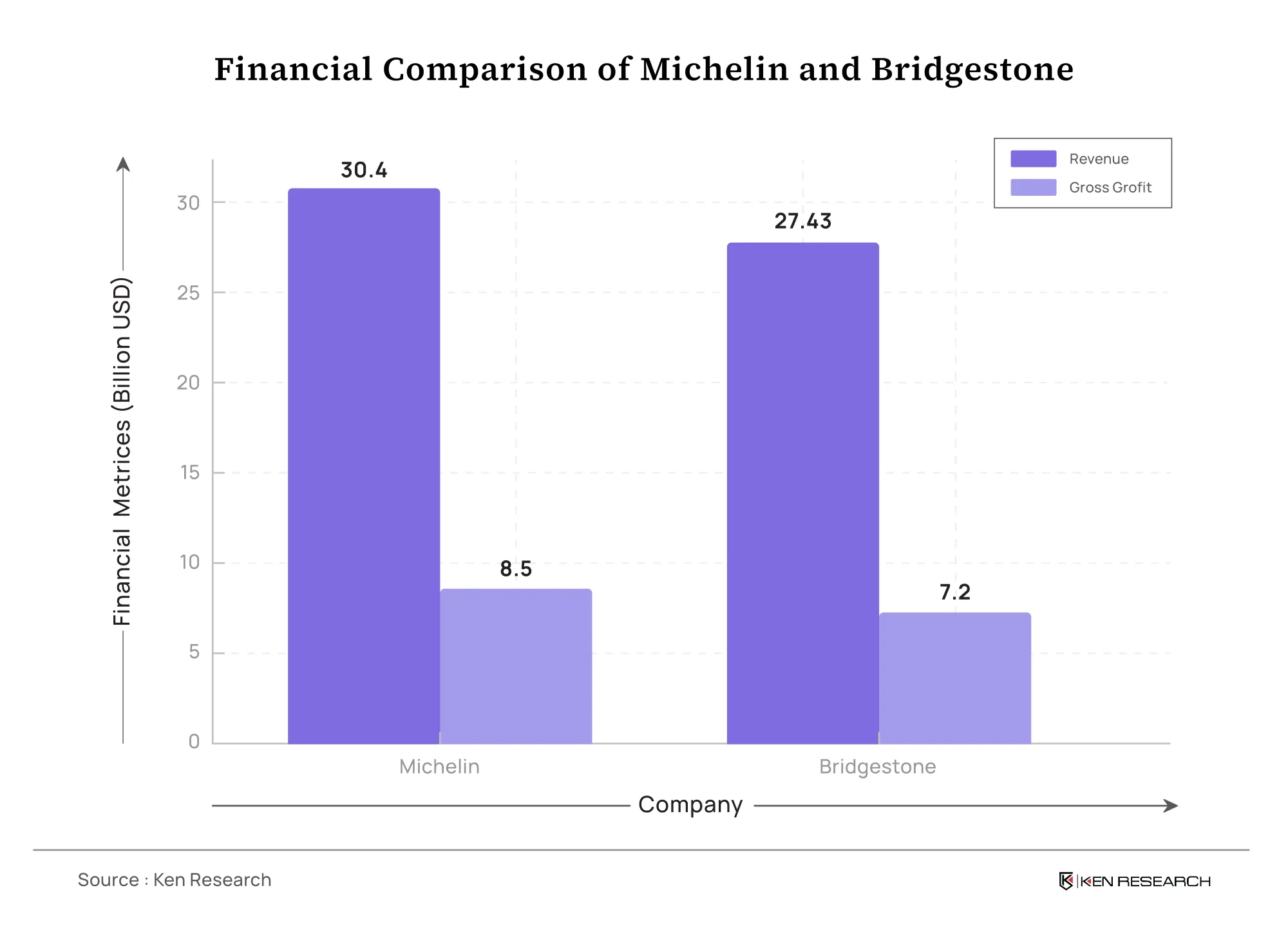
Profitability: While Michelin’s gross profit is reported at USD 8.5 billion, it appears to be focusing heavily on operational efficiency and its established position in the premium tire market. On the other hand, Bridgestone is allocating a significant portion of its earnings toward innovation and global expansion, reflecting a strategic emphasis on long-term growth.
Recent Innovations and Product Development
Company | Recent Innovations |
Michelin | Smart tire recycling solutions, lithium road cycling tires, eco-friendly tire technologies |
Bridgestone | Potenza Sport tires for Maserati’s all-electric SUV, Lunar Rover tire for NASA, AI-based tire intelligence technologies |
- Michelin’s Sustainability Leadership: Michelin’s commitment to sustainable tire production is showcased through innovations like smart tire recycling solutions and the development of lithium-based road cycling tires, a first in the industry. Michelin has partnered with Enviro to industrialize pyrolysis technology, which recycles end-of-life tires into regenerated materials like carbon black, oils, and gas. This reduces CO₂ emissions by over 90% compared to conventional methods.
- Bridgestone’s Performance Focus: Bridgestone’s innovations demonstrate its focus on high-performance and cutting-edge technologies. For example, its collaboration with Maserati to develop the Potenza Sport tire for luxury EVs showcases Bridgestone's emphasis on premium product offerings.
- Its work with NASA to develop the Lunar Rover tire highlights its leadership in technologically advanced solutions for non-traditional markets like space exploration. Bridgestone’s commitment to AI-based tire intelligence technologies further strengthens its position as an innovator in tire performance.
Commitment to Sustainability and ESG Leadership
Both companies have committed to advancing sustainability and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives:
- Michelin: Michelin has invested approximately USD 1.33 Bn in eco-friendly production methods, including tire recycling programs, which align with its broader vision of achieving carbon-neutral tire production. Michelin’s initiatives to reduce waste and use sustainable materials reinforce its image as an environmentally responsible brand.
- Bridgestone: Bridgestone has also introduced several sustainable tire technologies, such as the ContiTpu, a lightweight TPU inner tube made from sustainable materials. Bridgestone is just as committed to sustainability as Michelin, though its focus continues to be on high-performance products, with a strong emphasis on minimizing environmental impact.
Comparison of Michelin, Bridgestone and Competitors
Category | Michelin | Bridgestone | Continental | Goodyear | Sumitomo |
Regional Revenue Distribution | Dominates North America, strong in premium passenger & commercial tire segments | Dominates North America in premium passenger & commercial tire segments | Stronghold in Europe, diversified into automotive systems | Dominates in North America, particularly in OEM and replacement markets | Focuses on cost-effective production in emerging markets |
R&D Expenditures | Leads in R&D expenditure, focuses on sustainability & green technologies | Invests in innovations but prioritizes operational expansion | Diversified R&D into automotive systems and safety technologies | Focuses on cost-effective production strategies in emerging markets | Invests less in R&D, focusing more on production |
Gross Profit | Highest gross profit margin, focuses on premium products | Focuses on high-margin, high-performance and luxury segments | Varied, with a strong focus on automotive systems and safety technologies | Lower margins, strong in North America | Focuses on cost-effective production with lower margins |
- Michelin and Bridgestone stand out from their competitors due to their strong positions in premium tire markets, particularly in North America, where both companies dominate in the passenger and commercial tire segments. Michelin leads in total revenue and R&D expenditures, showcasing its commitment to sustainability and green technologies.
- Bridgestone, while slightly behind in R&D, has a significant focus on innovation, especially in high-performance products. Both companies have efficient operations, allowing them to maintain high gross profit margins, setting them apart from competitors like Goodyear, Continental, and Sumitomo, which have different regional focuses and investment priorities.
What does the Future hold?
In conclusion, Michelin and Bridgestone are industry leaders with different approaches: with USD 30.4 Bn in total revenue, Michelin concentrates on attaining recognition for sustainable and eco-friendly approaches to tire production that incorporate innovations in tire recycling and low-carbon production methods. Bridgestone has a revenue output of USD 27.43 Bn and is mostly concerned with high-performance tires and technology, including AI, with innovations such as the Lunar Rover tire.
Both firmly situated at the center of premium tire sales, Michelin is more focused on sustainability, whereas Bridgestone is on performance. Their strong market presence, high gross margins performance, and relevant R&D costs position them for competitive advantages. The tire sector is being changed by electric mobility and sustainability. Both Michelin and Bridgestone stand on this brink of transformation and will be able to much more efficiently utilize these trends to sustain their leadership positions.


