Industry 5.0: The Automation of future with Human-Centric, Sustainable, and Resilient Manufacturing
Over the years industrial revolution has seen incredible turnovers, from a 400% increase in the textile manufacturing to the adoption of Bessemer process, from advancement in steel production reaching an all-time high of 28 million tons by 1900 to the introduction of IT systems.

Nations globally are swiftly adopting Industry 5.0, the promise of increased productivity along with work safety and the ambition for sustainability is driving the economic growth. The adoption of sensible automation is making the rounds with an active vigilance towards global environment.
Over the years industrial revolution has seen incredible turnovers, from a 400% increase in the textile manufacturing to the adoption of Bessemer process, from advancement in steel production reaching an all-time high of 28 million tons by 1900 to the introduction of IT systems, digitization, and automation in the 2000’s it has proved to revolutionize the industrial framework in and out.
The introduction of Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution brought automation in the form of IoT, AI, robotics, it also paved the way fo smart machines, and factories to enhance efficiency, flexibility, and customization. This transformation improved overtime and and brought excellent real-time data analysis, leading to smarter, more efficient production systems gradually improving the decision-making capabilities across various industries.
The fifth and the upcoming Industry 5.0 perfectly aligns with its consequent goal which countries are trying to achieve, whether it is maximum profit without forgetting sustainability or optimal use of resources, these strategies are covering it all. Let us know further about it:
Industry 5.0: Carving its way as a Next level Industry
Industry 5.0 is promoting environmental responsibility, integrating technologies like AI, IoT, and collaborative robots. It champions the Triple Bottom Line: People, Planet, and Profit. From optimizing resilience and agility to decreasing the company’s downtime and inventory waste, Industry 5.0 is planning to ensure a robust supply chain even in crises.
- Synergy of Human and AI with Human Centricity: It focuses on viewing employees as valuable investments rather than costs. This approach has proven to enhance productivity and reduce workplace injuries through sensible automation. By integrating collaborative robots (cobots) and advanced sensors, the industry ensures safer and more efficient working environments, allowing humans to focus on creative and high-skilled tasks.
- The green core of Industry 5.0: The whole new need for sustainability in the latest environment has emphasized Industry 5.0 to align with the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the Triple Bottom Line (TBL) of People, Planet, and Profit. The key focuses of these concepts is on net zero carbon emissions within and reduce scrap/wastage by up to 50%, which will enhance resource efficiency, minimize environmental impact, and will supports long-term profitability.
- Resilient manufacturing system: Resilience has been a whole new psychological focus. It is the way of optimizing operations for agility and flexibility to maintain essential supplies during crises. Key strategies to this approach include reducing operational downtime by 25-30% and optimizing inventory management to cut stockpiling and wastage by 40-50%. This involves leveraging advanced analytics, IoT, and AI for predictive maintenance and real-time inventory tracking.
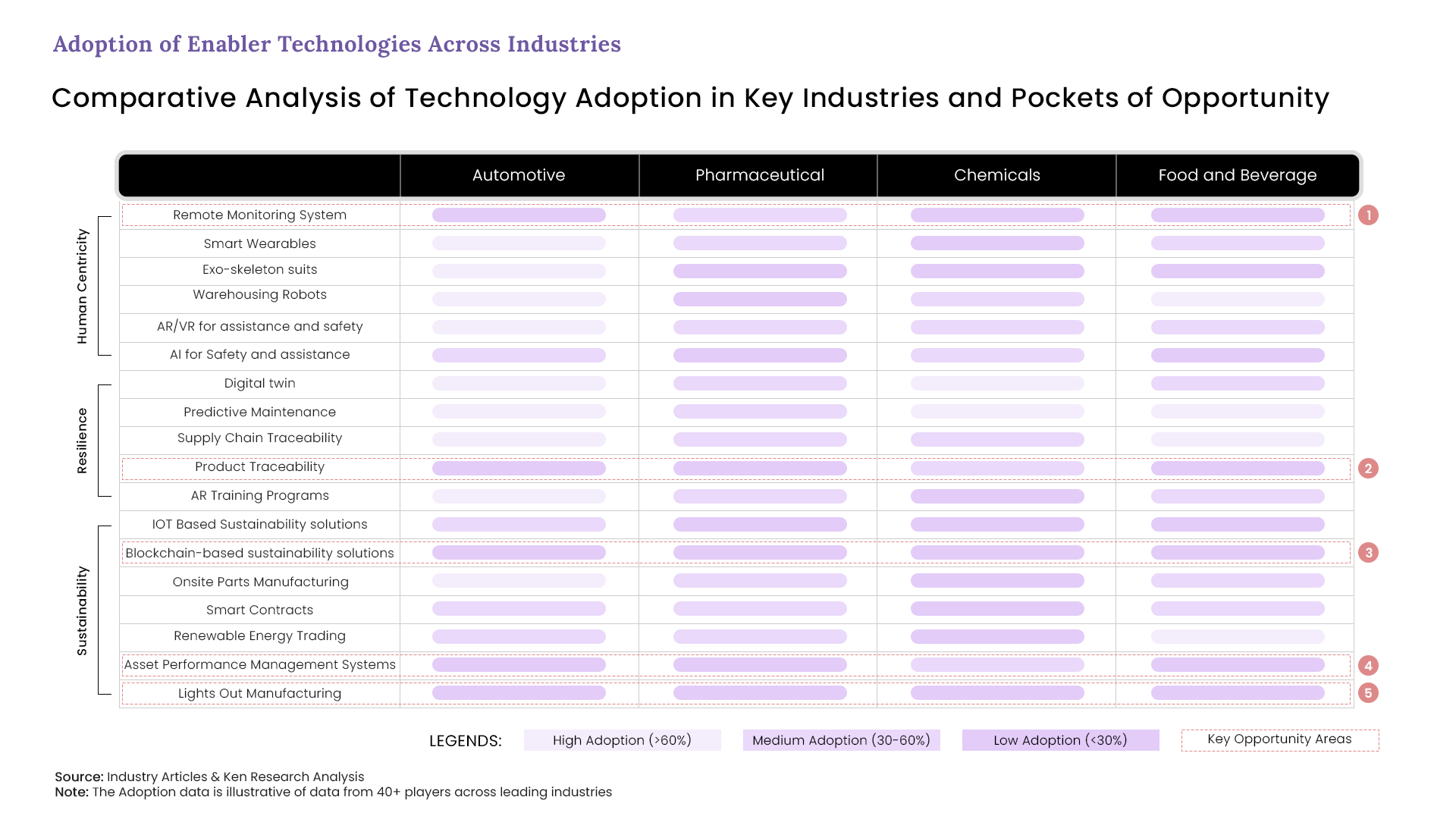
Human-centricity aims to enhance productivity by up to 25% and reduces workplace injuries by 70%. Smart Wearables Industries which include smart watches, smart glasses are empowering workers while assistance and safety is provided through the AR/VR the Remote Monitoring system. The remote monitoring system on the other hand is enabling real-time oversight and predictive maintenance, which enhances operational efficiency and reduces downtime which ultimately creates a safer and productive work environment creating a buzz.
Resilient Manufacturing is preparing for tomorrow’s challenges today. It is revolutionizing industries by incorporating technologies such as digital twins, predictive maintenance, and AR training programs to enhance operational stability and adaptability. Product traceability plays a dominant role, providing end-to-end visibility of a product’s journey throughout the supply chain. This ensures quality control, compliance, and swift response to issues, fostering a resilient and reliable production environment.
The 17 SDGs and the Triple Bottom Line to achieve net zero carbon emissions within 5-10 years. It is transforming industries through technologies like Blockchain solutions which dominates by ensuring transparent emissions monitoring and control. While asset performance management systems optimizes the resources used and minimize waste, while lights-out manufacturing enhances efficiency with fully automated operations, reducing energy consumption and emissions without human intervention, fostering a greener industrial environment.
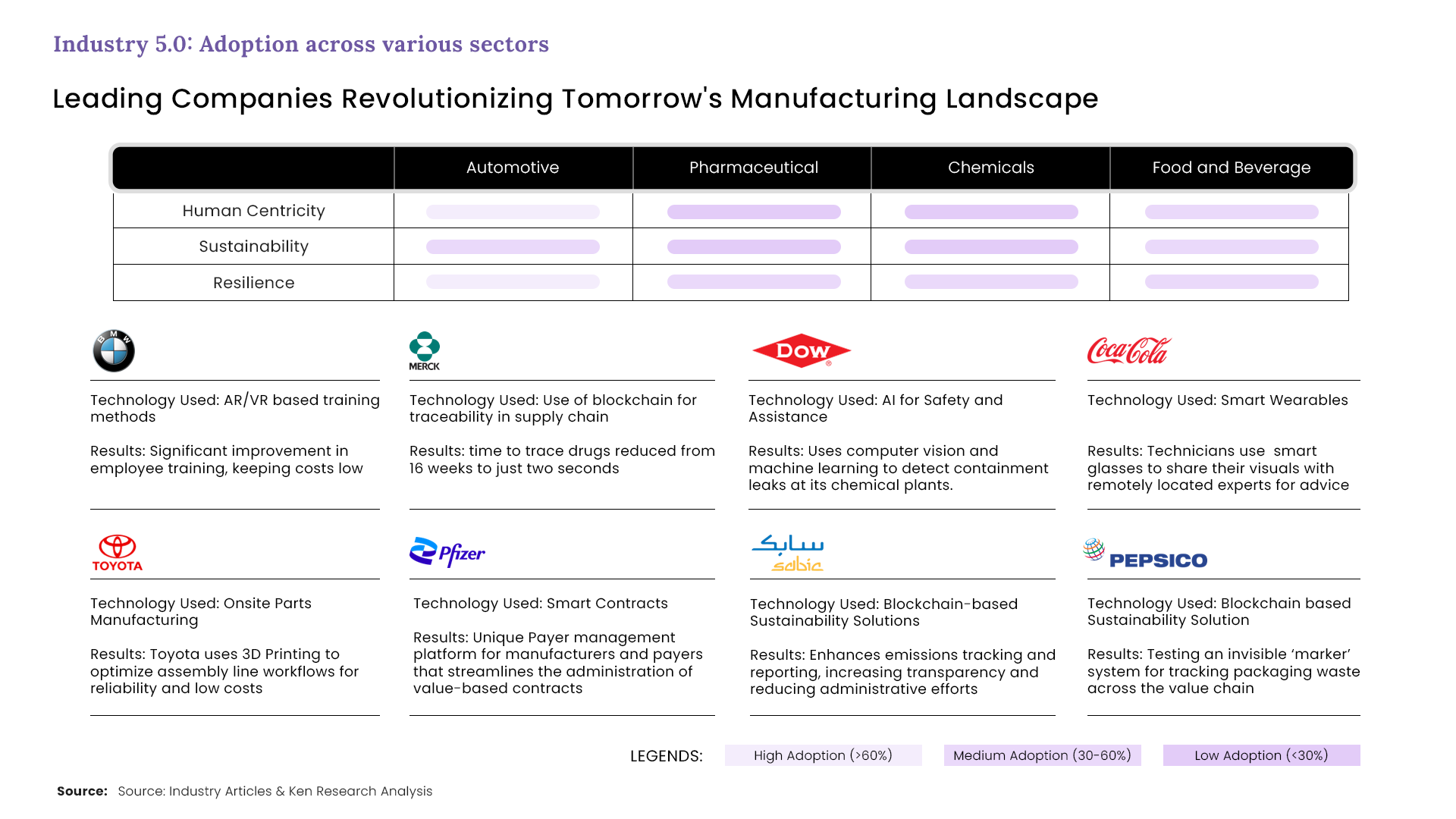
While Industry 5.0 is standing on these three pillars, leading companies in different sectors to use these to their own advantage by adopting each as per their convenience. Automotive industries are highly seeking human centricity and resilience, while balancing with sustainability. On the other hand, food and beverage industry is working on all the three pillars and building a strong foundation.
Pharmaceuticals and chemicals industry are still to adopt the measures given by Industry 5.0, while they believe in resilience and adopting it slowly, there is still low adoption of human centricity and sustainability in both these sectors.
Challenges & Risks in the Workforce and Technology Integration
Even when these industries are flourishing and there is a lot of risk involved in Workforce and Technology Integration, here are some challenges that the companies will face in the future-
- Workforce Polarization- While high-skilled job opportunities increase, Sectors heavily reliant on low-skilled labor, such as manufacturing and logistics, are expected to see job reductions of up to 10-15% by 2030.
- Skill Development Hurdles- By 2027, 60% of workers will need training, but currently, only half of them have access to sufficient training opportunities.
- Worker Safety Concerns- The introduction of collaborative robots has resulted in a 15% rise in reported safety incidents, with 30% of factories reporting incidents involving human-robot interaction in the past year.
- Data Quality and Integration- Businesses typically allocate 20-30% of their IT budgets to integrate diverse data sources, with manufacturing systems incurring higher costs due to complex data from supply chains, production lines, and quality control.
- Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities- Organizations globally faced an average annualized cybercrime cost of $13 million. Within this, the manufacturing industry ranked second, experiencing an average annual cost of $7.91 million.
Even though the challenges seem to be a barrier in the path for growth there are various key opportunities that have potential to grow, the graph is a representation of how, Industry 5.0 implementation holds over USD 40 billion potential with emerging adoption across.
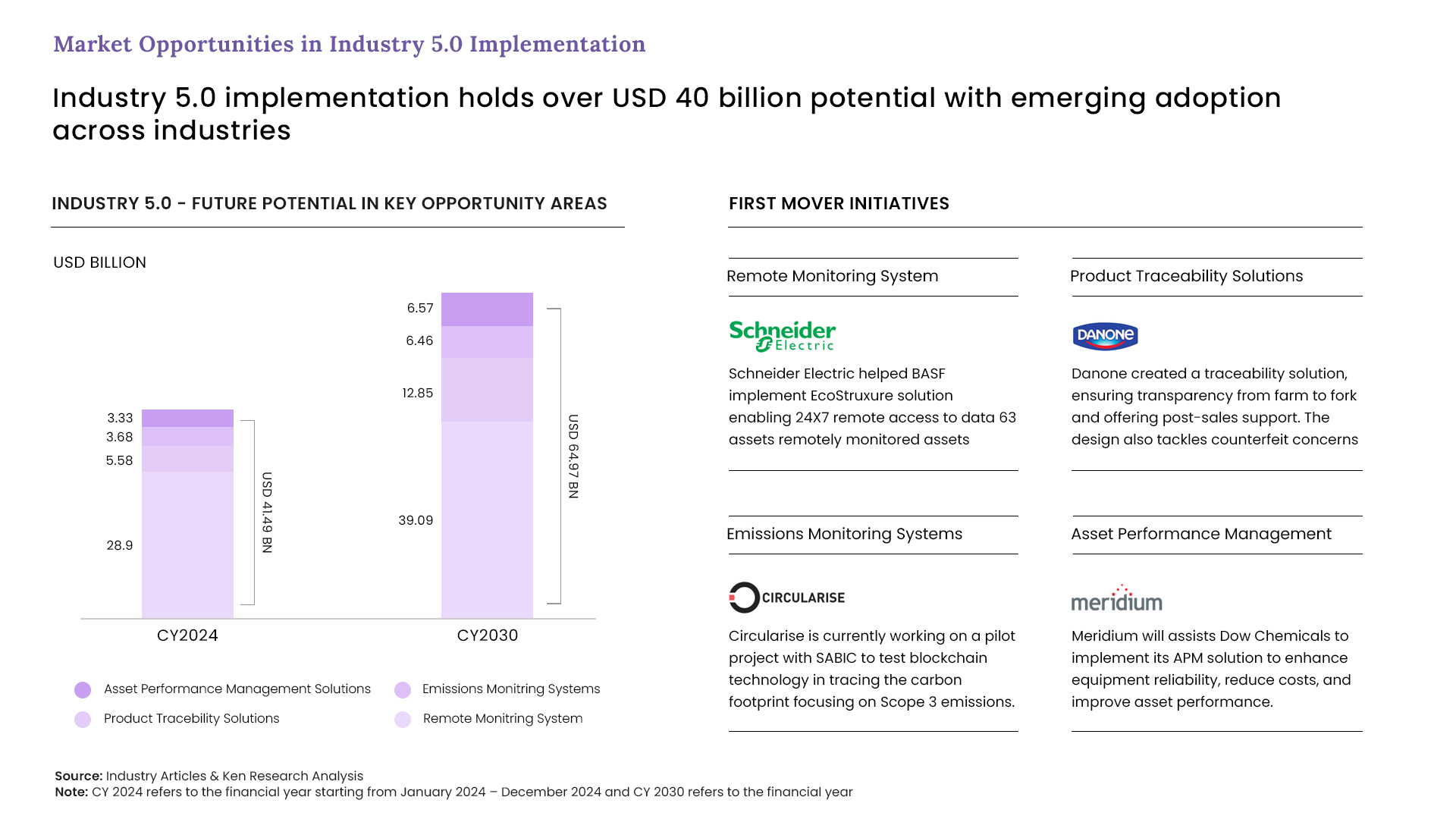
There is a lot of future potential in the areas like remote monitoring system, asset performance management solutions, emission monitoring systems and product traceability solutions. As depicted in the graph remote monitoring system has reached a valuation of USD 28.9 billion and growing extensively with an expected market size of USD 39.09 billion. Companies across various industries are adopting expertise in these areas and taking their first mover advantage, here are some examples-
Electric helped BASF implement EcoStruxure solution enabling 24X7 remote access to data 63 assets remotely monitored assets
Danone created a traceability solution, ensuring transparency from farm to fork and offering post-sales support. The design also tackles counterfeit concerns
Circularise is currently working on a pilot project with SABIC to test blockchain technology in tracing the carbon footprint focusing on Scope 3 emissions.
Meridium will assists Dow Chemicals to implement its APM solution to enhance equipment reliability, reduce costs, and improve asset performance.
Conclusion
Industry 5.0 combines technological advancements with human-centric and sustainable practices to boost productivity, safety, and environmental responsibility. It presents opportunities for growth and innovation while posing challenges. The key question is how organizations will leverage these advancements to remain competitive and contribute to a sustainable, prosperous future.
Key Uncertainties:
The growing concern over work polarization is reshaping the job market, especially as low-skilled positions diminish, leading to uncertainty for many workers. While the introduction of collaborative robots enhances safety in industrial environments, it also brings challenges related to training and the complexities of managing cyber vulnerabilities. Different sectors, such as automotive, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals, are grappling with questions about how uniformly and quickly they can adopt Industry 5.0 technologies. As technology advances rapidly, the demand for higher skills increases, making it difficult for training programs to keep pace and effectively prepare workers for the evolving landscape.
Big Questions about the future
How can companies ensure their workforce is prepared for the shift towards more automated and intelligent systems? What role will collaboration with technology providers and other industries play in an organization's Industry 5.0 strategy? How can businesses measure the impact of Industry 5.0 on their sustainability goals? What investments are necessary for companies to successfully transition to Industry 5.0? How can organizations use Industry 5.0 to improve customer experience and satisfaction? What steps can businesses take to stand-in a culture of continuous learning and adaptability in an Industry 5.0 environment?


